USPS Mail Carrier Delivers Support for Stray Cat
Mail carrier built outdoor shelter, contacted ARL to rescue and rehome
The Animal Rescue League of Boston (ARL) would like to acknowledge an incredible act of kindness that took place amid the holiday delivery rush in early December.
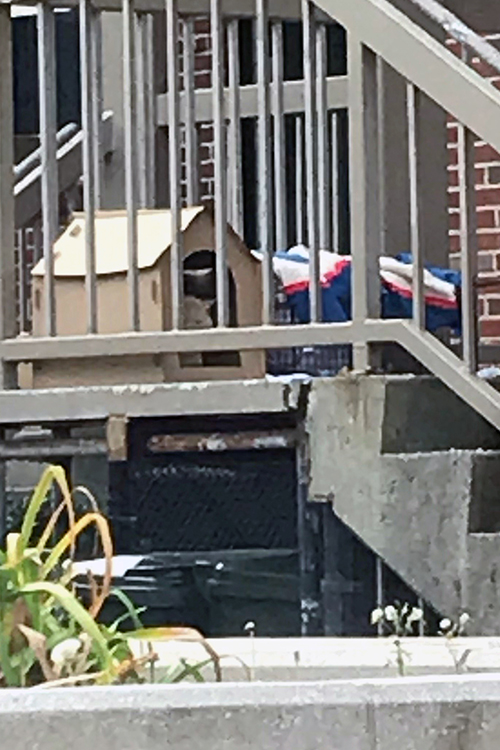
While delivering mail, a compassionate, yet anonymous, United States Postal Service mail carrier in Cambridge, MA, went above and beyond their duties to deliver special support for a friendly stray in the Jackson Circle area.
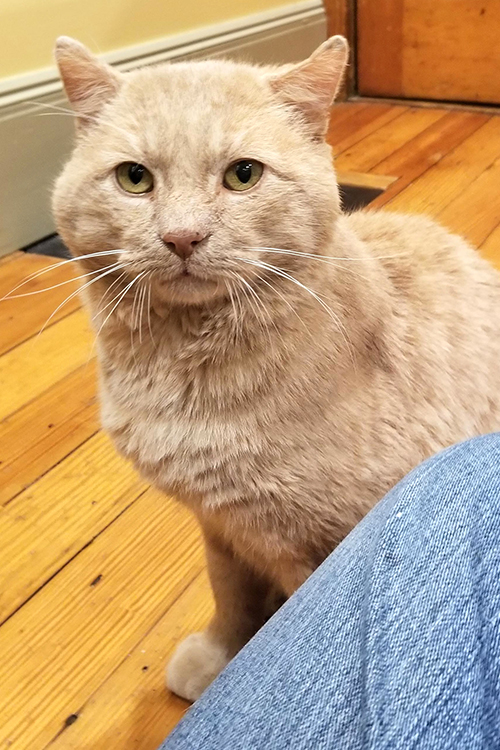
The mail carrier was not only feeding the cat, later named Jackson, but had also constructed a cardboard shelter to help protect the animal from the elements.
As temperatures dipped and winter began to take hold, showing great concern for Jackson, the mail carrier contacted ARL’s Field Services Department to rescue the cat from a life on the streets.
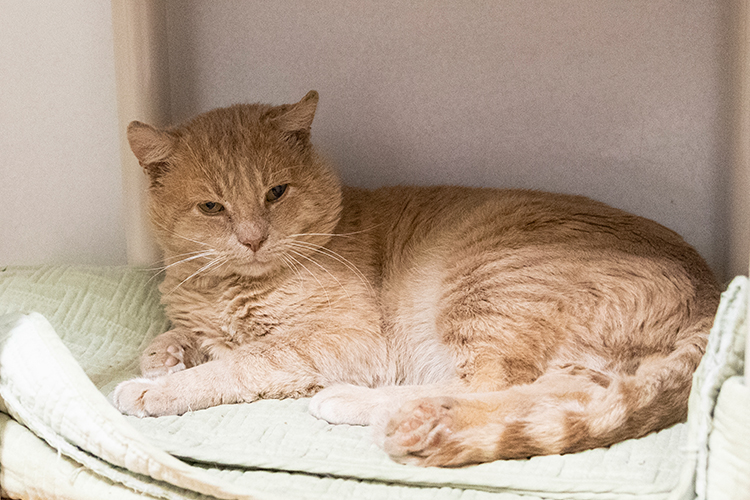
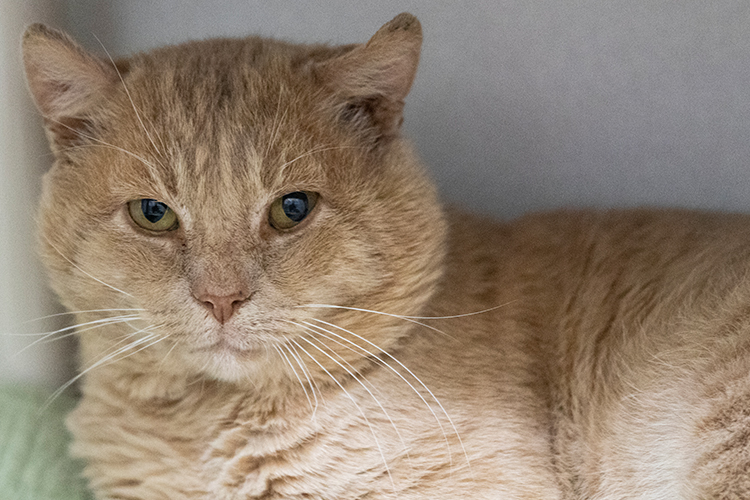
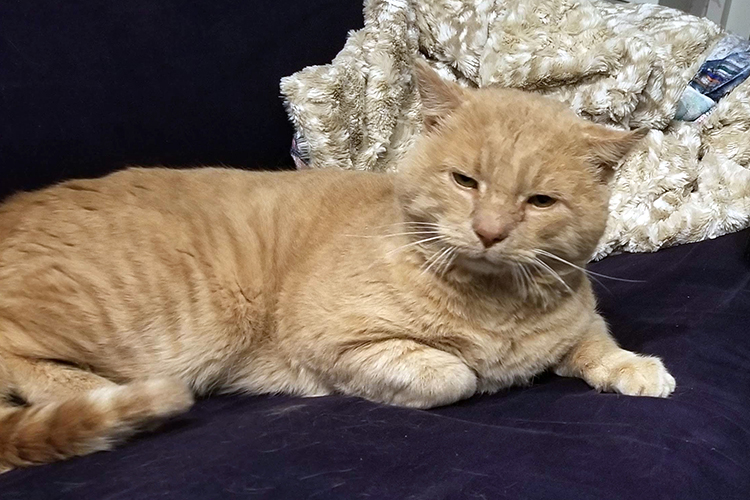
Jackson, who’s estimated to be eight-years-old, was extremely friendly when approached by ARL Field Services staff, and was brought to ARL’s Boston Animal Care and Adoption Center.
A thorough veterinary exam revealed extensive dental disease, to the point where all but one of Jackson’s canines were cracked down to the root.
Additionally Jackson had a number of abrasions, and tested positive for Feline Immunodeficiency Virus, which cannot be transmitted to humans but can be spread via bite wounds between cats. It should be noted that cats who test positive for FIV do go on to lead normal and healthy lives.
ARL shelter medicine staff performed a deep dental cleaning on Jackson, and because of the severity of his dental disease, 10 teeth needed to be extracted.
After recovering from his medical procedures, Jackson quickly found his forever home just in time for the holidays, and is thriving in his new environment under a new name – Teddy!
ARL is grateful to this anonymous mail carrier and their incredible act of compassion and kindness to not only look after Jackson but to make sure he didn’t have to spend another winter on the tough streets of Boston.